Table of Contents
It is typical, yet can be extremely significant, impacting how you really feel, assume, and act. Having scientific depression is different than just really feeling sad. It is a relentless feeling of sadness, despondence, and loss of passion. To be identified with clinical depression, signs have to exist for two weeks or even more.

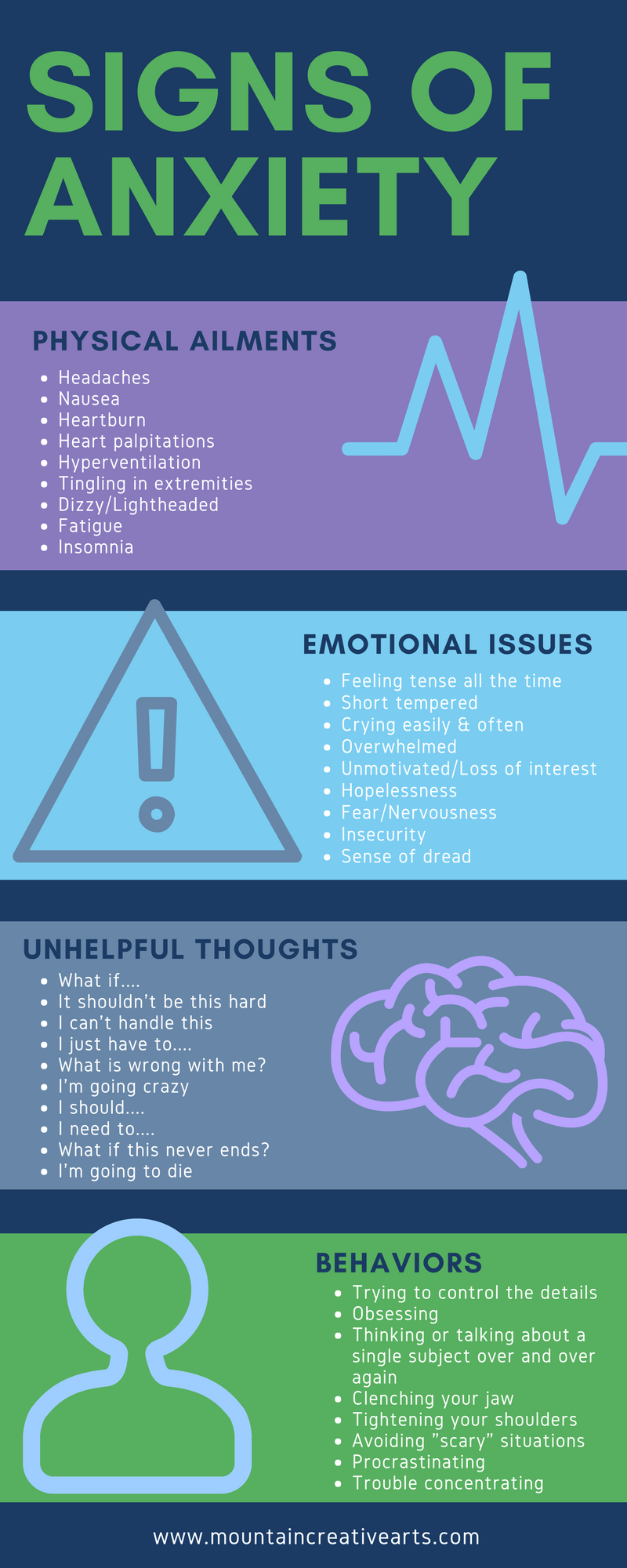
From person to person the intensity and regularity of signs will differ, and while some people only experience a couple of signs and symptoms, others experience several. Consistent unfortunate, nervous, or "vacant" state of mind Really feeling helpless Feeling worthless Angry outbursts, impatience, or stress Loss of interest or satisfaction in hobbies and activities Thinking nothing is worth attempting Thinking of death, or that life is unworthy living Absence of energy Moving or talking slower than normal Difficulty with focus, emphasis, memory, and choice making Feeling troubled or having difficulty sitting still Hunger or weight changes Difficulty resting, early-morning awakening, or resting a lot more or a lot less than typical Aches or discomforts, migraines, cramps, or digestive system problems without a clear physical cause Although anxiety is one of the most usual mental illness in the US, there is no exact recognized reason of anxiety.
Discovering Emotional Pain By Means Of Clinical Therapy
Danger variables for depression include: Acquired qualities, individual or family background of depression Environmental elements, like major life modifications, injury, or tension Psychological factors Particular physical diseases and drugs Biological distinctions, brain chemistry, or hormones The most efficient treatment for clinical depression is drug and psychiatric therapy. The earlier that depression is dealt with, the easier it is to deal with.
Talking with a psychiatrist, psycho therapist or various other psychological health expert, can be very valuable for people with clinical depression. Drugs to treat clinical depression are called antidepressants. There are many type of antidepressants that do different points in the mind, like improve just how the mind uses certain chemicals, or maintain your mood.
Investing in Emotional Resilience With Specialized Perinatal Mental Health Services
Some instances of antidepressants are: Careful serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) Atypical antidepressants Tricyclic antidepressants Monoamine oxidase preventions (MAOIs) Yes, you can have stress and anxiety and depression at the same time. Although they are two separate and unique psychological health problems, they commonly happen concurrently. Sometimes, a person can have both a stress and anxiety condition and a major depressive disorder.
In other situations, clinical depression may create stress and anxiety. They are two interrelated mood conditions, and often there is some degree of overlap. Yes, there is a distinction between stress and anxiety and depression medication. There are anti-anxiety medicines especially for treating anxiety signs and symptoms, and antidepressants particularly for treating depression symptoms. One type of medication that has revealed to be effective in treating stress and anxiety and clinical depression are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Person-Centered Modalities for Overcoming Perinatal Mental Health Services Through Brainspotting
Treatment can be a helpful tool for individuals with anxiety and anxiety. For both anxiety and depression, CBT involves talking via habits patterns, and assists to show people with these mental ailments how to deal with signs.
The bulk of dealing with anxiety and depression with therapy is overlapping. Using evidence-based techniques specific to the treatment of state of mind disorders, like CBT, and regularly speaking to a specialist will certainly aid those with stress and anxiety, clinical depression, or both, make noticeable improvements.
Why Traumatic Experiences and Depression
Mental health and wellness is complicated. While specialists have actually developed specific diagnoses for various sorts of disorders, the truth is that several disorders have a large amount of overlap, which can make it rather challenging to separate in between 2 different issues. Among one of the most usual concerns that people have is attempting to discriminate between stress and anxiety and clinical depression.
While it would be excellent if there were a fool-proof way of informing you whether you have anxiety or anxiety, it's not rather that straightforward. Someone can easily have both anxiousness and depression, and some people may have established clinical depression signs as an outcome of their anxiety condition. It's a bit harder than stating "you have stress and anxiety" or "you have clinical depression" because it's feasible to have mixes of both.
Symptoms of one or the various other might bleed right into whichever problem you have, due to the fact that both share similar causes, problems, etc. The ideal method to comprehend the difference between the two disorders is with the main signs and symptoms, starting with the mental signs. Anxiousness: Uneasiness over what's about to happen and what might take place in the future.
Recognizing Attachment Theory Affects Relationship Issues
Feeling like you require to run away or stay clear of points that might create additional stress and anxiety. Depression: Feeling of unhappiness about the future, as though it's hopeless.
Those with anxiety typically assume a negative future and don't expect anything else or assume there's anything worth protecting against. Clinical depression can happen after somebody experiences anxiety, since somebody that deals with serious stress and anxiety might wind up feeling drained pipes and helpless when their anxiety or anxiousness attack is over. That's why the two conditions can be tough to inform apart.
Both anxiety and anxiety can leave you feeling drained and fatigued. In the instance of anxiety, it often tends to happen after extreme stress and anxiety, while with depression it often tends to be extra constant, without necessarily any kind of triggers.
Physical signs and symptoms that appear like wellness conditions, especially if accompanied with health concerns. Rapid heart rate, digestive tract issues, hyperventilation, and other "power" triggering symptoms. Depression: Severe lack of power or drive. Level affect (total lack of emotion) along with slowed down thinking and actions. Severe appetite changes, headaches, and sleep issues. Anxiety in fact tends to have less physical signs, yet the mental signs and symptoms can be so unsafe (especially the possibility for suicidal thoughts) and the absence of power so articulated that lots of individuals with depression manage intense battles daily that absolutely competing the signs and symptoms of anxiety.
Navigation
Latest Posts
Understanding the Brain Science of Complex Trauma
Understanding of Bereavement
Exposure-Based EMDR Therapy for Dual Diagnoses